In scanning target network is probed for getting information.
Main Objective of network scanning:
- Identify live hosts on a network
- Identify open ports
- Identify OS and system architecture
- Identify process and services running
- Identify security devices like firewalls
This information help us in identifying vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
Nmap is one of the most popular scanner available.
Scanning Methodology:
- Host Discovery(checking for live systems) - with Ping sweep scan
nmap -sn [TARGET/CIDR]
- Port scanning
Port scanning is used to probe a server or host for open TCP and UDP ports.
nmap -sS -sU [TARGET]
can be used to scan top 1000 TCP (-sS) and Udp (-sU) ports.
-
Scanning beyond IDS/IPS/firewalls
Fragmentation and small packets can be used to evade security devices.
IDS have reassemble these packets to detect and inspect them.
These small packets can be made complicated to reassemble or we can send fragmented packets out of order with pauses to create delay -
Fingerprinting
Fingerprinting is the process of identifying the services connected to the ports.
Active - OS Fingerprinting
nmap -O [TARGET]
Passive - Banner Grabbing
nmap --script=banner [TARGET]
- Vulnerability Scanning
- Network Diagram
- Prepare Proxies
Proxy system helps in hiding scanner's identity.
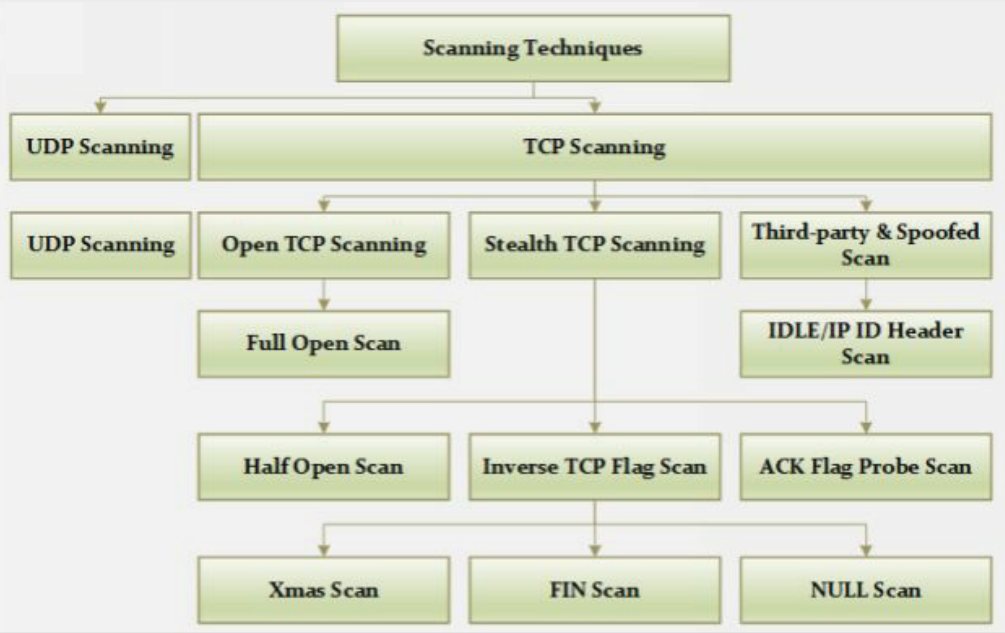
Different types of Scanning
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) scan
This scan helps us in network mapping and discovering active devices on the network.
In it, a series of ARP broadcast is sent, and the value for the target IP address field is incremented in each broadcast packet.
Vanilla TCP connect scan
It is the basic scanning technique that uses connect system call of an operating system to open a connection to every port that is available.
TCP SYN (Half Open) scan
In it state of a port is determined without establishing a full connection. These scans are called half open because the attacking system doesn’t close the open connections.
TCP FIN Scan
This scan can remain undetected through most firewalls, packet filters, and other scan detection programs. It sends FIN packets to the targeted system and prepares a report for the response it received.
TCP XMAS Scan
It is used to identify listening ports on the targeted system. The scan manipulates the URG, PSH and FIN flags of the TCP header.
UDP ICMP Port Scan
This scan is used to find UDP ports but it is slow and unreliable.